Introduction
Tinea manuum is a common fungal infection of the hands, caused by dermatophyte fungi. It mainly affects the palms, fingers, and back of the hands. This condition is often confused with eczema or psoriasis because of similar symptoms like dryness and scaling. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are important to prevent spreading.
TINEA MANUUM
What Is Tinea Manuum?
Tinea manuum is a type of ringworm (dermatophytosis) that specifically involves the skin of the hands. It may affect:
- One hand (most common)
- Both hands (less common)
NOTE ,:-
It is frequently associated with tinea pedis (athlete’s foot), a condition known as “one hand – two feet syndrome.”
Causes
Tinea manuum is caused by fungi called dermatophytes, mainly:
- Trichophyton rubrum
- Trichophyton mentagrophytes
- Epidermophyton floccosum
These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments and feed on keratin present in the skin.
How Does It Spread?
The infection spreads through:
- Direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person
- Contact with contaminated objects such as towels, gloves, or gym equipment
- Scratching infected feet and then touching hands
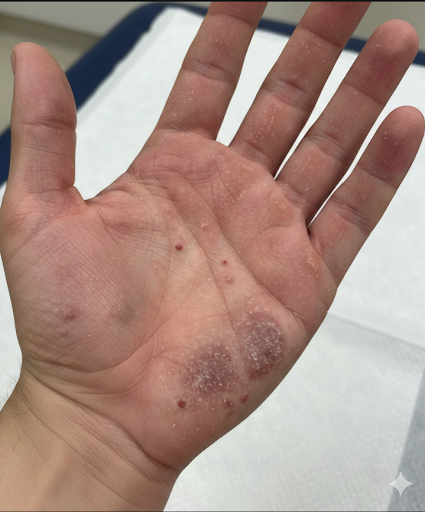
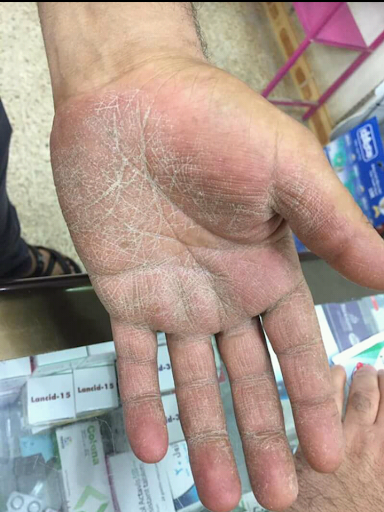
Signs and Symptoms
Common symptoms include:
- Dryness and scaling of the palms
- Itching (may be mild to severe)
- Thickened skin on the palm
- Red patches with clear borders
- Peeling skin, especially along skin creases
- Sometimes small blisters
NOTE :-It often affects only one hand, while both feet may be involved ( i.e. called as one hand and both feet syndrome)
Who Is at Risk?
People more likely to develop tinea manuum include:
- Farmers, laborers, and people who work with soil or animals
- Athletes and gym users
- Diabetic patients
- People with weak immunity
- Those with poor hand hygiene
Diagnosis
Doctors usually diagnose tinea manuum by:
- Clinical examination
- Skin scraping and microscopic examination (KOH test)
- Fungal culture in some cases
Treatment
1. Topical Antifungal Creams (for mild cases)
Apply for 2–4 weeks:
- Clotrimazole
- Terbinafine
- Ketoconazole
- Miconazole
2. Oral Antifungal Medicines (for severe or chronic cases)
Prescribed by a doctor:
- Terbinafine
- Itraconazole
- Fluconazole
- Griseofulvin
💡 NOTE :-
Always complete the full course of treatment to prevent recurrence.
Home Care and Preventive Tips
- Keep hands clean and dry
- Avoid sharing towels, gloves, or personal items
- Wash socks and towels in hot water
- Treat foot fungal infections simultaneously
- Avoid scratching affected areas
- Use antifungal powder if excessive sweating is present
Complications
Untreated tinea manuum can lead to:
- Secondary bacterial infection
- Spread to other body parts
- Chronic thickening and cracking of skin
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. Is tinea manuum contagious?
Yes, it is contagious and spreads by direct or indirect contact.
Q2. Can it be cured completely?
Yes, with proper antifungal treatment and hygiene, it can be completely cured.
Q3. How long does it take to heal?
Usually 2–4 weeks with regular treatment. Chronic cases may take longer.
Q4. Can it come back after treatment?
Yes, recurrence is possible if hygiene is poor or if foot infection is not treated.Q5. Can home remedies cure it?
Home remedies may help symptom relief, but antifungal medication is necessary for complete cure.
Conclusion
Tinea manuum is a common but easily treatable fungal infection of the hands. Early treatment, good hygiene, and prevention of reinfection are key to complete recovery.




