Introduction
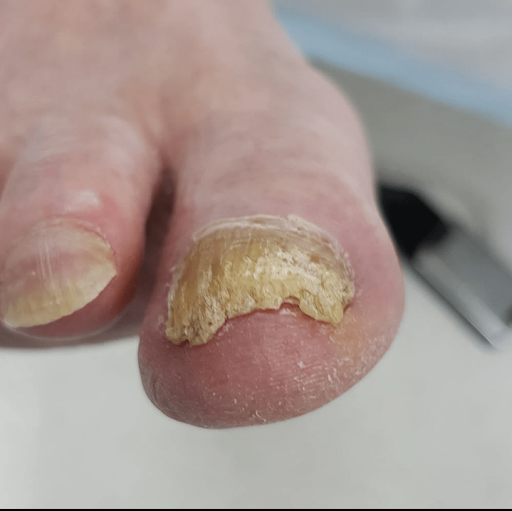
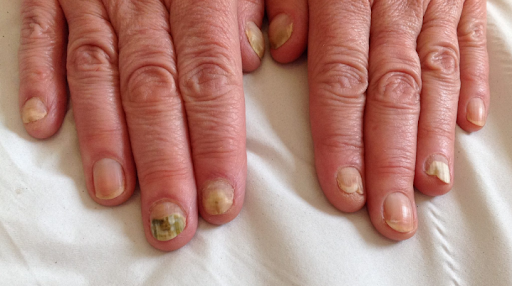
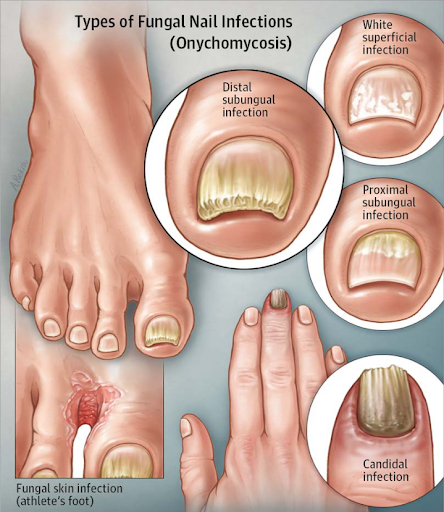
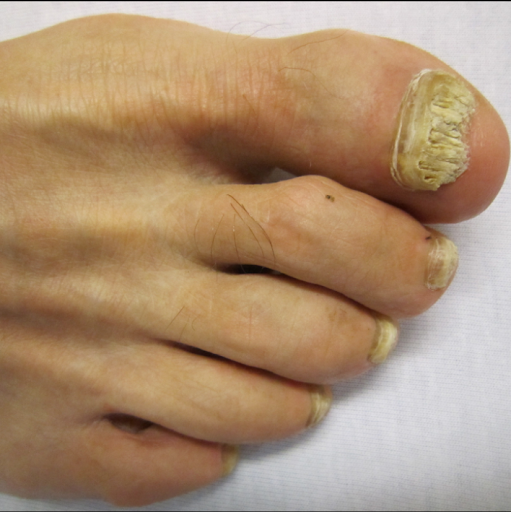
Tinea unguium, also known as Onychomycosis, is a common fungal infection of the nails. It usually affects the toenails but can also involve fingernails. The infection makes nails thick, discolored, brittle, and weak, and if left untreated, it can spread to other nails and skin.
TINEA UNGUIUM (ONYCHOMYCOSIS)
Causes
This condition is mainly caused by dermatophyte fungi, but yeast and molds can also be responsible.
Common causes include:
- Walking barefoot in public places like bathrooms, swimming pools, and gyms
- Excessive sweating of feet
- Wearing tight or non-breathable shoes
- Poor nail hygiene
- Nail trauma or injury
- Sharing nail clippers, towels, or socks
- Weak immune system
Who is at Risk?
People more prone to developing Tinea unguium:
- Elderly individuals
- Diabetic patients
- People with poor circulation
- Those with long-standing tinea pedis (athlete’s foot)
- People with suppressed immunity
- People who wear closed shoes for long hours
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on severity but commonly include:
- Yellow, white, or brown discoloration of nails
- Thickened nails
- Brittle or crumbly nail edges
- Distorted nail shape
- Separation of nail from nail bed (onycholysis)
- Bad smell
- Pain in advanced stages
Is Tinea Unguium Contagious?
Yes, it is contagious. It can spread by:
- Direct contact with infected nails
- Sharing nail tools, towels, socks, and shoes
- Using common floors in bathrooms and swimming pools
Diagnosis
Doctors may confirm the condition through:
- Nail scraping for KOH test
- Fungal culture
- Microscopic examination
Treatment
1. Topical Antifungal Medicines
Useful in mild cases:
- Amorolfine nail lacquer
- Ciclopirox nail lacquer
- Efinaconazole solution
Apply regularly for several months.
2. Oral Antifungal Medicines (For moderate to severe cases)
- Terbinafine
- Itraconazole
- Fluconazole
⚠️ NOTE :-
These must be taken under medical supervision due to potential liver side effects.
3. Nail Care
- Keep nails short and clean
- Remove dead infected nail parts
- Keep feet dry
Home Remedies
These can help along with medical treatment:
- Tea tree oil (diluted)
- Apple cider vinegar foot soaks
- Coconut oil application
- Keeping feet dry and clean
⚠️ NOTE :-
Home remedies are supportive, not a replacement for antifungal medicine.
Prevention
- Keep feet clean and dry
- Wear breathable footwear
- Avoid walking barefoot in public areas
- Do not share nail clippers, socks, or towels
- Change socks daily
- Use antifungal powder if prone to sweating
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. Is Tinea unguium same as nail fungus?
Yes, Tinea unguium is the medical term for fungal nail infection.
Q2. Can it heal on its own?
No, it usually does not go away without proper treatment.
Q3. How long does treatment take?
It may take 3–6 months for fingernails and 6–12 months for toenails.
Q4. Can I use nail polish during infection?
It is best to avoid nail polish as it locks moisture and delays healing.
Q5. Is it dangerous?
Generally not dangerous, but can cause pain, secondary infection, and spread if untreated.
Q6. Can it come back after treatment?
Yes, recurrence is possible if proper hygiene is not maintained.
Conclusion
Tinea unguium is a common but treatable fungal nail infection. Early diagnosis and regular treatment can prevent complications and spread. Maintaining good nail hygiene and foot care is key to prevention and recovery.




