Introduction
Herpes simplex is a common viral infection caused by the Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV). It mainly affects the skin and mucous membranes, producing painful blisters or ulcers. Once infected, the virus remains in the body in a latent (sleeping) state and can reactivate from time to time.
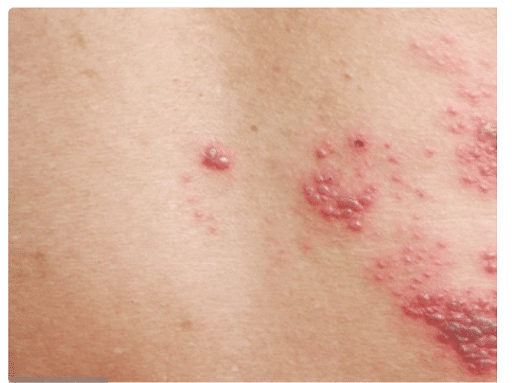
Types of Herpes Simplex Virus
- HSV-1 (Herpes Simplex Type 1)
- Commonly causes oral herpes
- Affects lips, mouth, face
- Known as cold sores / fever blisters
- HSV-2 (Herpes Simplex Type 2)
- Mainly causes genital herpes
- Affects genital and anal areas
- Usually transmitted through sexual contact
NOTE :-
HSV-1 can also cause genital herpes due to oral-genital contact.
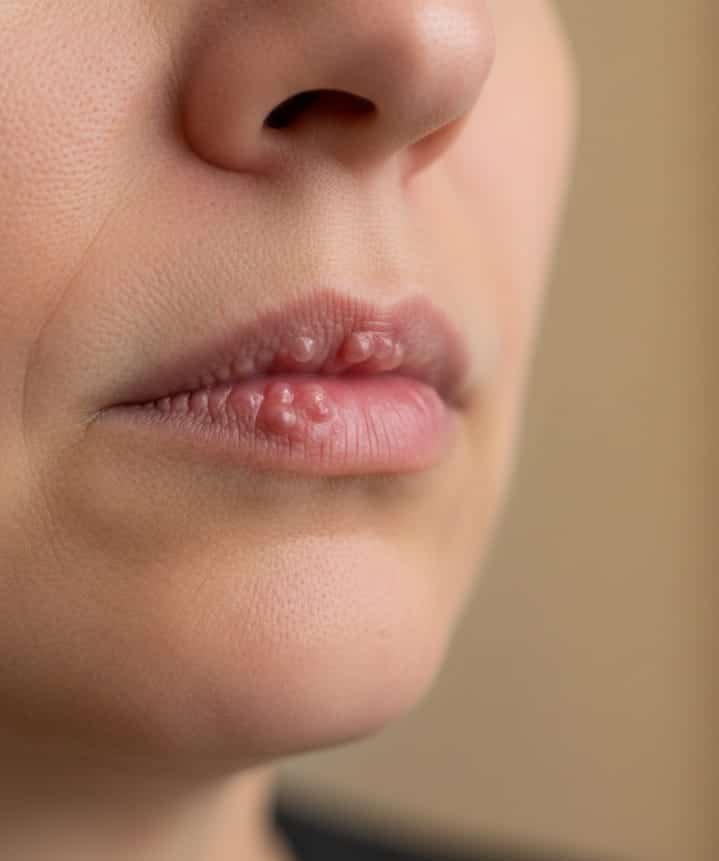

HERPES LABIALIS
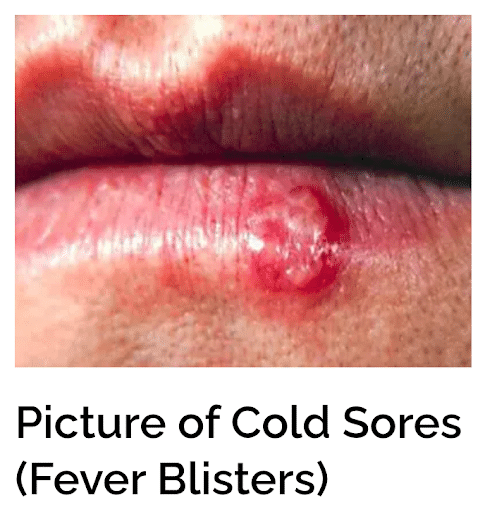
Mode of Transmission
Herpes simplex spreads through direct contact with infected secretions or lesions:
- Kissing
- Oral-genital or genital-genital contact
- Sharing towels, razors, lip balm (rare but possible)
- Mother to baby during childbirth (rare but serious)
Clinical Features (Symptoms)
Primary Infection
- Fever
- Malaise, body ache
- Painful grouped vesicles (small blisters)
- Burning or tingling sensation
- Swollen lymph nodes
Recurrent Infection
- Mild symptoms
- Localized blisters
- Healing within 7–10 days
Common Sites of Lesions
- Lips and mouth
- Nose
- Genital area
- Buttocks
- Thighs
- Fingers (Herpetic whitlow)
Diagnosis
- Clinical examination (most common)
- Tzanck smear – shows multinucleated giant cells
- PCR test – most sensitive
- Viral culture
- Serology (HSV-1 & HSV-2 antibodies)
Treatment
Modern Medicine
- Acyclovir
- Valacyclovir
- Famciclovir
These medicines:
- Reduce severity
- Shorten duration
- Decrease recurrence frequency
Note: There is no permanent cure, but proper treatment controls the disease effectively.
Ayurvedic View (Brief)
In Ayurveda, herpes simplex is related to Pitta and Rakta dushti. Management includes:
- Rakta shodhan
- Pitta shamak aushadhi
- Local soothing applications
- Lifestyle and dietary correction
Prevention
- Avoid contact during active lesions
- Use condoms (reduces risk, not 100%)
- Maintain good immunity
- Avoid stress and fatigue
- Do not share personal items
Complications
- Secondary bacterial infection
- Recurrent painful episodes
- Neonatal herpes (if transmitted to newborn)
- Severe disease in immunocompromised patients
Conclusion
Herpes simplex is a chronic but manageable viral infection. Early diagnosis, proper treatment, and lifestyle modification help in reducing symptoms and preventing frequent recurrences. Awareness and preventive measures play a key role in controlling its spread.




