Introduction
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It commonly affects the genital tract, but can also infect the rectum, throat, and eyes. If not treated early, gonorrhea can lead to serious complications in both men and women.
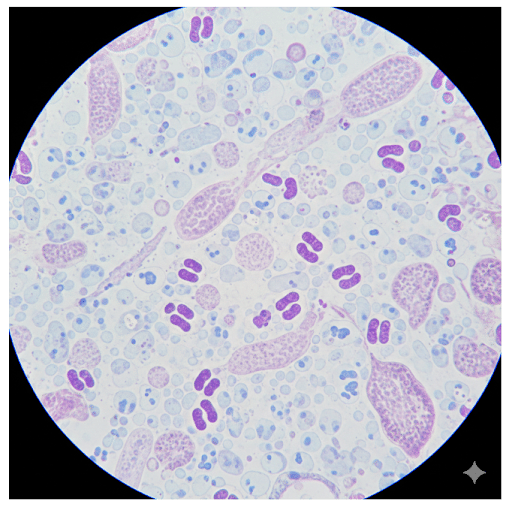
GONOCOCCAL BACTERIA – UNDER MICROSCOPE
How Gonorrhea Spreads
Gonorrhea is transmitted through:
- Unprotected vaginal sex
- Anal sex
- Oral sex
- From mother to baby during childbirth
NOTE :-
It does not spread through casual contact like hugging, sharing food, or using the same toilet.
Symptoms of Gonorrhea
In Men
- Burning or pain during urination
- Thick white, yellow, or green discharge from penis
- Pain or swelling in one testicle
- Rectal pain or discharge (if rectal infection)
In Women
- Increased vaginal discharge
- Pain or burning during urination
- Lower abdominal pain
- Pain during intercourse
- Irregular menstrual bleeding
⚠️ NOTE :-
Many women have no symptoms, making regular testing important.
Throat Gonorrhea
- Sore throat
- Mild irritation
- Often asymptomatic
Complications of Untreated Gonorrhea
In Women
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
- Infertility
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Chronic pelvic pain
In Men
- Epididymitis
- Infertility (rare but possible)
In Both
- Increased risk of HIV infection
- Disseminated gonococcal infection ( joint pain, skin lesions )
Diagnosis of Gonorrhea
- Urine test
- Swab test (cervix, urethra, rectum, or throat)
- NAAT (Nucleic Acid Amplification Test) – most accurate
- Culture test (important for antibiotic resistance)
Treatment of Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is curable with antibiotics.
Standard Treatment
- Injectable Ceftriaxone
- Sometimes combined with oral antibiotics
⚠️ NOTE :-
Self-medication should be avoided due to increasing antibiotic resistance.
Partner Treatment
- Sexual partners from the last 60 days should be tested and treated.
- Avoid sexual activity for 7 days after treatment and until partners are treated.
Prevention of Gonorrhea
- Use condoms consistently
- Limit number of sexual partners
- Regular STI screening
- Early treatment of infected partners
Gonorrhea in Pregnancy
- Can cause eye infection or sepsis in newborns
- Routine screening and early treatment are essential
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is gonorrhea curable?
Yes, gonorrhea is completely curable with proper antibiotics.
2. Can gonorrhea come back after treatment?
Re-infection is possible if exposed again to an infected partner.
3. Can gonorrhea be asymptomatic?
Yes, especially in women and throat infections.
4. Does gonorrhea affect fertility?
Yes, untreated gonorrhea can lead to infertility in both sexes.
5. Can condoms fully prevent gonorrhea?
Condoms significantly reduce risk but do not provide 100% protection.
Conclusion
Gonorrhea is a common but treatable STI. Early diagnosis, proper treatment, and partner management are key to preventing complications. Regular screening and safe sexual practices play a vital role in control and prevention.




