Introduction
Molluscum contagiosum is a common viral skin infection seen in children, young adults, and sexually active individuals. Although harmless, the condition can be cosmetically disturbing and contagious. It is caused by the Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV), a member of the poxvirus family.
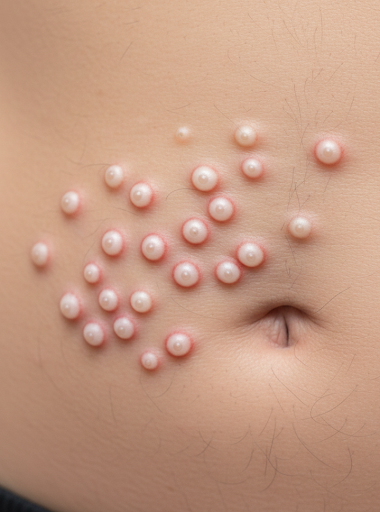
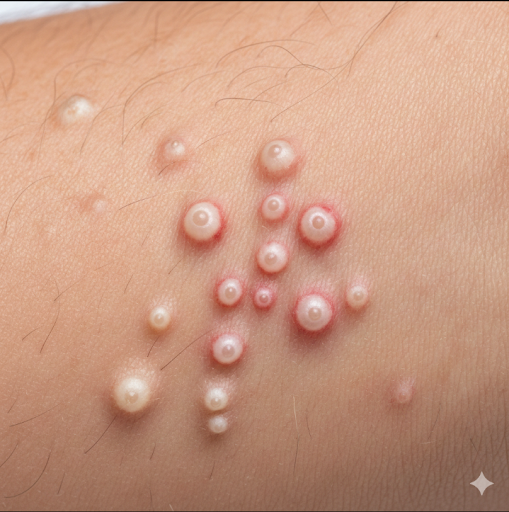
MOLLUSCUM CONTAGIOSUM
What is Molluscum Contagiosum?
Molluscum contagiosum presents as small, smooth, round, dome-shaped papules with a central umbilication (tiny pit).
These bumps are:
- Skin-colored or pearly-white
- 2–5 mm in size
- Painless
- Often grouped
- Can appear anywhere on the body
Causes
The disease is caused by the Molluscum Contagiosum Virus (MCV).
Transmission occurs through:
✔ Skin-to-skin contact
- Common in children
- Sexual contact in adults
✔ Contaminated objects
- Towels
- Razors
- Clothes
- Wrestling mats
✔ Autoinoculation
Scratching the bumps spreads them to nearby skin.
Who is at Risk?
- Children (most common)
- People with eczema
- Athletes (wrestlers, swimmers)
- Immunocompromised individuals
- Sexually active adults (genital molluscum)
Symptoms
Typical features include:
- 1–20+ flesh-colored bumps
- Smooth, shiny surface
- Central dimple (umbilication)
- Mild itching at times
- Redness if inflamed or infected
- Can appear on face, arms, trunk, legs
- In adults: may appear on genital area
Complications
Most cases are harmless, but complications may include:
- Secondary infection
- Spread to other body areas
- Scarring after scratching or removal
- Chronic lesions in people with weak immunity
Diagnosis
Molluscum contagiosum is usually diagnosed clinically by its characteristic appearance.
Dermatologists may use:
- Dermatoscopy
- Scraping/curettage for microscopic exam (rarely needed)
NOTE :-
No blood test is required.
Treatment Options
Although molluscum can resolve naturally in 6–12 months, treatment is recommended to prevent spread.
1. Physical treatments
- Curettage (scraping out the lesion)
- Cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen)
- Radiofrequency cautery
- Laser ablation
2. Topical Medications
- Potassium hydroxide solution (10–15%)
- Tretinoin 0.025–0.05%
- Salicylic acid
- Iodine + salicylic acid combination
- Imiquimod (less commonly used)
3. Ayurvedic Approach
Ayurveda focuses on immunity boosting, local healing, and preventing spread.
✔ Internal Medicines (commonly used)
- Guduchi (Giloy)
- Neem
- Turmeric (Haridra)
- Triphala
- Khadirarishta
NOTE :-
Should be used under physician guidance.
✔ External Applications
- Neem oil
- Haridra powder paste
- Panchvalkal kwath wash
Home Remedies
These remedies may help reduce spread and speed up healing:
- Apply tea tree oil (diluted).
- Avoid scratching.
- Keep skin clean and dry.
- Use separate towels & razors.
- Cover lesions during sports.
Prevention
- Avoid sharing towels, razors, or sports gear
- Maintain good personal hygiene
- Avoid shaving over bumps
- In children: keep nails trimmed
- Safe sexual practices (for genital lesions)
When to See a Doctor
- Lesions persist beyond 6 months
- Rapid spreading
- Painful, red, or infected bumps
- Genital lesions
- If you have diabetes, eczema, or low immunity
Conclusion
Molluscum contagiosum is a mild but contagious viral skin condition. Early identification and proper treatment help prevent spread and scarring. Both modern dermatology and Ayurvedic therapies offer effective solutions.




