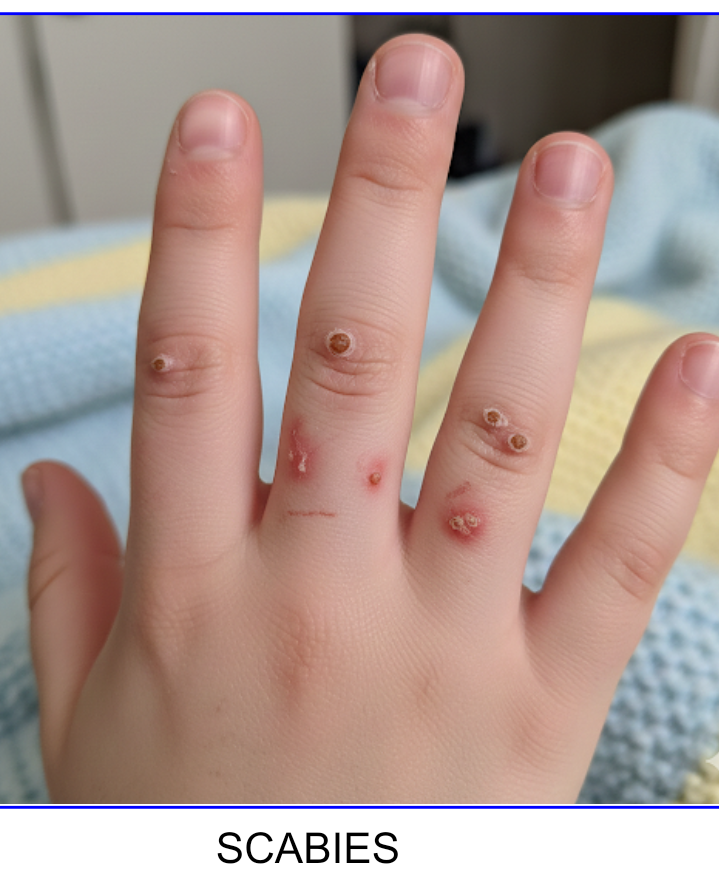
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by a tiny insect-like parasite called Sarcoptes scabiei. These mites burrow into the upper layer of the skin, causing intense itching, rashes, and discomfort. Scabies can affect people of all ages, but spreads more easily in crowded places, families, hostels, hospitals, and children.
What is Scabies?
Scabies is a skin infection where microscopic mites live and lay eggs inside the skin. The body’s reaction to the mites causes redness, intense itching, and small bumps or burrows.
It spreads mainly through prolonged skin-to-skin contact.
Causes
The main cause is an infestation by the scabies mite. It spreads through:
- Close physical contact with an infected person
- Sharing clothes, towels, or bedding
- Living in crowded places
- Sleeping in the same bed as someone with scabies
Who is at Risk?
Anyone can get scabies, but risk is higher in:
- Children
- Elderly people
- People living in hostels or crowded homes
- People with weaker immune systems
- Nursing home residents
- People who share clothes or bedding frequently
Signs & Symptoms
1. Intense itching – especially at night
2. Small red bumps or rashes
3. Thin, wavy burrows on the skin
4. Sores from scratching
Common areas affected
- Hands and fingers
- Wrists
- Waistline
- Underarms
- Around nipples (in women)
- Genital area (in men)
- Buttocks
- Feet (especially in infants)
Is Scabies Contagious?
Yes! Scabies is very contagious.
It spreads quickly from one person to another through close contact. Entire families can get infected if one member has scabies.
Diagnosis
A dermatologist can diagnose scabies by:
- Examining the skin rash
- Identifying burrows
- Sometimes scraping the skin to see mites or eggs (rarely needed)
Prevention
- Avoid sharing clothes, towels, or bedding
- Wash clothes and bed linens in hot water
- Iron clothes to kill mites
- Maintain personal hygiene
- Treat ALL family members at the same time
- Vacuum mattresses and sofas
Home Remedies (Supportive Only)
These help relief but do not cure scabies. Medicine is necessary.
- Neem oil
- Aloe vera gel
- Tea tree oil (not for kids under 6 years)
- Clove oil
- Cold compress to reduce itching
Medical Treatment
Scabies can be completely cured with proper medication.
1. Permethrin 5% Cream
- Most commonly used treatment
- Apply from neck to toes at night
- Leave for 8–12 hours and wash off
- Repeat after 1 week
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can scabies spread by shaking hands?
Yes, if contact is prolonged. Short quick touches usually don’t spread sUsually 24 hours after starting treatment, but all clothes and bedding must be washed.
cabies.
2. Can scabies spread through pets?
No. Dogs and cats have different mites that do not survive on human skin.
3. Is itching normal even after treatment?
Yes. Itching can continue for 2–4 weeks after successful treatment as the body reacts to dead mites.
4. When can I go to school/work again?
Usually 24 hours after starting treatment, but all clothes and bedding must be washed.
5. Can home remedies cure scabies?
No. They only reduce itching. Medicines are essential to kill mites.
6. Do I need to wash everything?
No. They only reduce itching. Medicines are essential to kill mites.
7. Do I need to wash everything?
Yes. Clothes, towels, bedsheets must be washed in hot water and sun-dried.
8. Is scabies serious?
Not usually, but severe forms (crusted scabies) need urgent treatments