Introduction
Tinea Barbae is a fungal infection of the beard and moustache area, commonly seen in adult males. It is caused by dermatophyte fungi that infect hair follicles and surrounding skin. The infection usually spreads from animals (especially cattle) or from infected humans.
NOTE :-
If not treated early, it may lead to deep inflammation and scarring. The good news—Tinea barbae responds well to proper antifungal treatment.
TINEA BARBAE
Causes
Tinea Barbae is caused by dermatophyte fungi, mainly:
- Trichophyton verrucosum (from cattle)
- Trichophyton mentagrophytes
- Microsporum canis (from pets like cats & dogs)
Risk Factors
- Farmers, dairy workers, veterinarians
- Close contact with infected animals
- Sharing razors, trimmers
- Poor hygiene
- Weak immune system
- Already having fungal infections on other body parts
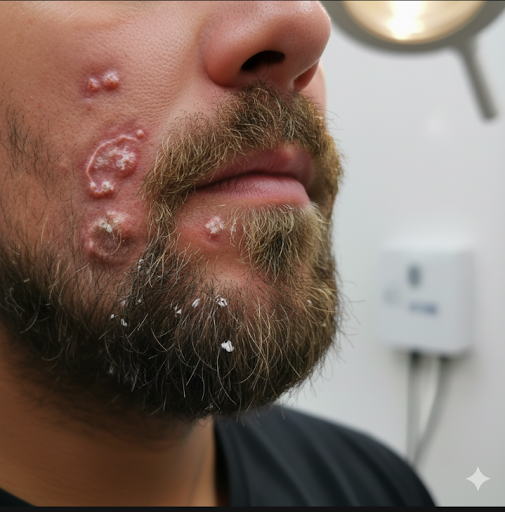
Signs & Symptoms
Tinea Barbae shows two types of lesions:
1. Inflammatory Type (Deep Infection)
- Red, swollen, painful nodules in beard area
- Pus-filled bumps
- Easily pluckable beard hairs
- Thick crusting
- Fever may occur sometimes
- Looks similar to bacterial folliculitis
2. Non-Inflammatory Type
- Dry, scaly patches in beard area
- Mild itching
- Patchy hair loss
- Broken beard hairs
- Ringworm-like circular lesions
Diagnosis
A dermatologist may use:
- KOH test: Scraping examined under microscope
- Fungal culture: To identify exact fungus
- Dermatoscopy: To see hair changes
- Clinical examination: Based on appearance
Treatment
Tinea Barbae usually requires oral antifungal medication, because topical creams alone are not enough.
1. Oral Antifungal Medicines
Commonly prescribed by dermatologists:
- Terbinafine 250 mg once daily for 4–6 weeks
- Itraconazole 100–200 mg daily for 4–6 weeks
- Griseofulvin in some cases
(Dosage and duration must be decided by a qualified doctor.)
2. Topical Antifungal Creams
Used along with oral medicines:
- Ketoconazole 2% cream
- Clotrimazole 1%
- Terbinafine 1%
3. Medicated Shampoos
For beard washing:
- Ketoconazole 2% shampoo
- Selenium sulfide 2.5% shampoo
4. Avoid
- Shaving infected area
- Sharing shaving tools
- Using steroid creams like betamethasone, quadriderm, panderm (they worsen infection)
Prevention
- Avoid close contact with infected cattle or pets
- Do not share razors or trimmers
- Keep beard area clean and dry
- Treat fungal infections on body immediately
- Regularly disinfect grooming tools
- While working with animals, use gloves and protective clothing
Complications
If untreated:
- Permanent hair loss in beard area
- Scarring
- Spread to other body parts
- Secondary bacterial infection
FAQ
1. Is Tinea Barbae contagious?
Yes. It spreads by skin-to-skin contact or through infected animals, razors, trimmers, towels, etc.
2. Can it be treated with home remedies?
Home remedies are not effective.
This infection needs oral antifungal medicines.
3. How long does it take to heal?
With proper treatment, symptoms improve in 1–2 weeks, and full recovery takes 4–6 weeks.
4. Can shaving worsen the infection?
Yes. Shaving can spread fungi and cause deeper infection.
5. Can women get Tinea Barbae?
It is extremely rare in women because they lack thick beard hair, but mild facial fungal infections can occur.




