What is Urethritis?
Urethritis is inflammation of the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. It commonly causes burning during urination and discharge from the penis or vagina. Urethritis can affect both men and women, though symptoms are more noticeable in men.
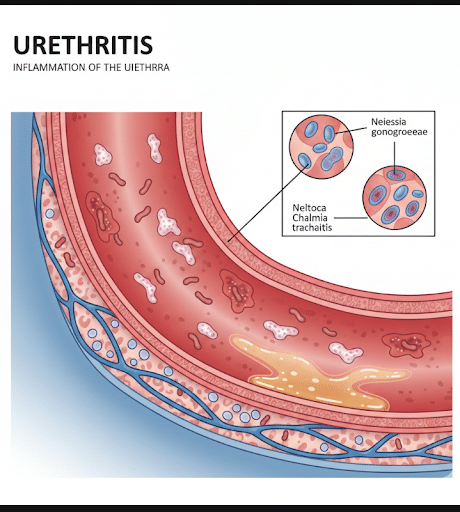
Urethritis
Types of Urethritis
1. Gonococcal Urethritis (GU)
- Caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- A sexually transmitted infection (STI)
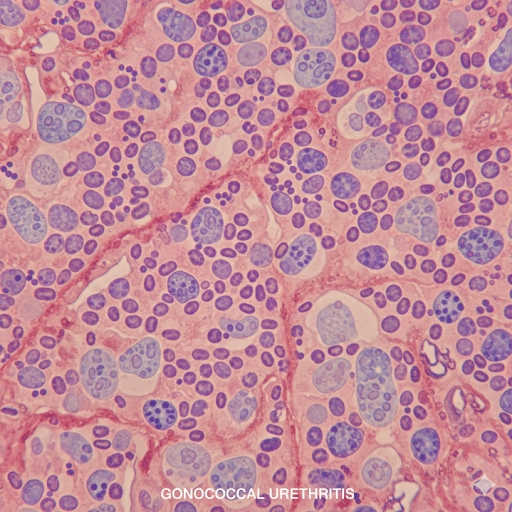
GONOCOCCAL URETHRITIS
2. Non-Gonococcal Urethritis (NGU)
Caused by organisms such as:
- Chlamydia trachomatis (most common)
- Mycoplasma genitalium
- Ureaplasma urealyticum
- Viruses (HSV)
- Irritation from chemicals, soaps, or catheters
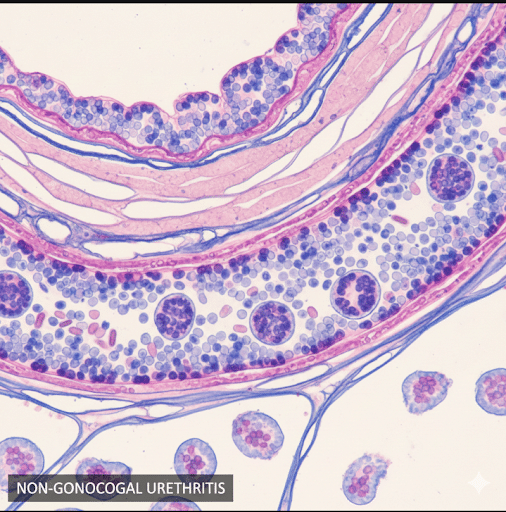
NONGONOCOCCAL URETHRITIS
Causes of Urethritis
- Unprotected sexual intercourse
- Multiple sexual partners
- Previous STI
- Poor genital hygiene
- Trauma or catheterization
- Chemical irritation (soaps, spermicides)
Symptoms of Urethritis
In Men
- Burning or pain during urination
- White, yellow, or green penile discharge
- Itching or irritation at urethral opening
- Pain during ejaculation
- Increased frequency of urination
In Women
- Burning during urination
- Increased vaginal discharge
- Lower abdominal pain
- Pain during intercourse
- Many women may be asymptomatic
Diagnosis of Urethritis
- Detailed sexual history
- Urine routine & microscopy
- First-void urine NAAT (PCR test)
- Urethral swab (in males with discharge)
- STI screening (HIV, syphilis)
Treatment of Urethritis
Treatment depends on the cause.
Empirical Treatment (Common Regimen)
- Azithromycin 1 g single dose
OR - Doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 7 days
For Gonorrhea
- Ceftriaxone injection (as per guidelines)
Supportive Care
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Avoid sexual activity until treatment completion
- Treat sexual partners simultaneously
⚠️ NOTE :-
Never self-medicate. Always consult a doctor.
Complications if Untreated
- Epididymitis
- Prostatitis
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Infertility
- Increased risk of HIV transmission
Prevention of Urethritis
- Use condoms consistently
- Limit sexual partners
- Regular STI screening
- Prompt treatment of partner
- Maintain genital hygiene
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. Is urethritis a sexually transmitted disease?
👉 Often yes, but not always. It can also be caused by non-sexual irritation or infections.
Q2. Can urethritis heal on its own?
👉 No. Antibiotics are usually required to prevent complications.
Q3. Is urethritis contagious?
👉 Yes, if caused by infection. It can spread through sexual contact.
Q4. How long does treatment take?
👉 Symptoms usually improve within 2–3 days, but the full course must be completed.
Q5. Can urethritis cause infertility?
👉 Yes, if untreated, especially in men and women with repeated infections.
Q6. Should my partner also take treatment?
👉 Yes, even if asymptomatic.
Q7. Can I have sex during treatment?
👉 No. Avoid sexual activity until treatment is completed and symptoms resolve.
Q8. Is urethritis common in women?
👉 Yes, but often goes unnoticed due to mild or absent symptoms.
Q9. Can urethritis recur?
👉 Yes, due to reinfection or incomplete treatment.
Q10. When should I see a doctor?
👉 If you have burning urination, discharge, or risky sexual exposure.
Conclusion
Urethritis is a common but treatable condition. Early diagnosis, proper antibiotics, and partner treatment are essential to prevent complications. Safe sexual practices play a vital role in prevention.




