Introduction
Vaginal yeast infection is a common fungal infection of the vagina caused mainly by Candida albicans. It affects women of all ages and is not usually serious, but it can cause significant discomfort and irritation if left untreated.
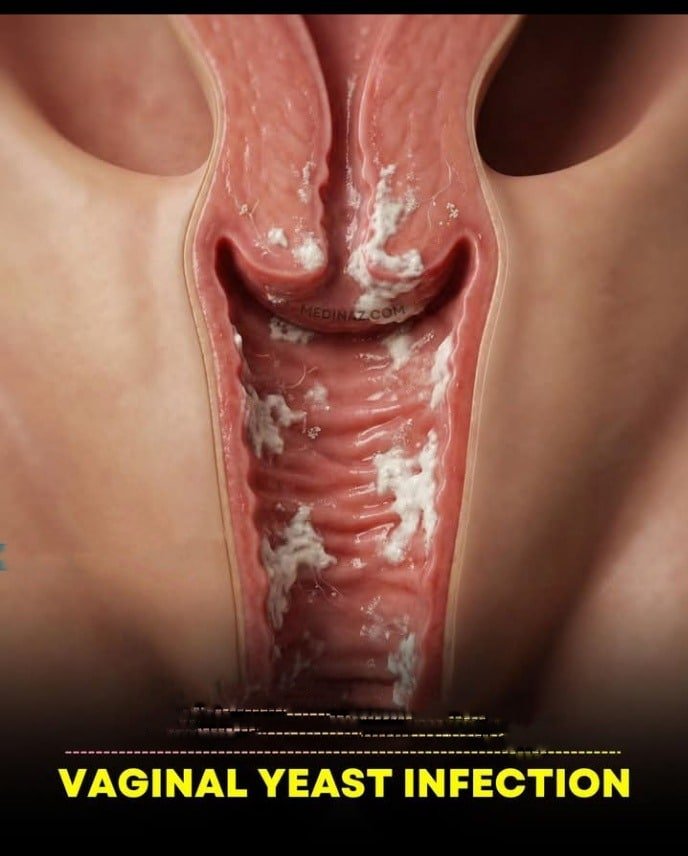
VAGINAL YEAST
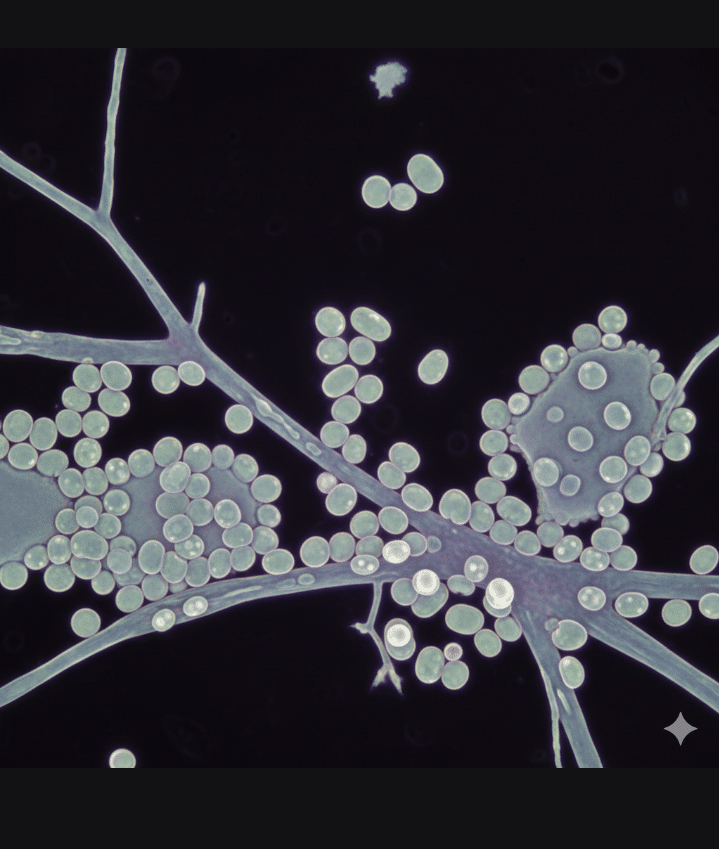
VAGINAL YEAST UNDER MICROSCOPE
What is a Vaginal Yeast Infection?
A vaginal yeast infection occurs when there is an overgrowth of Candida fungus in the vagina. Normally, yeast lives in small amounts in the vagina, but changes in the vaginal environment can allow it to multiply excessively.
Causes
Common causes include:
- Antibiotic use
- Pregnancy
- Diabetes (especially uncontrolled)
- Hormonal changes
- Weak immune system
- Tight or non-breathable clothing
- Excessive vaginal douching
- High estrogen levels (oral contraceptives, hormone therapy)
Symptoms
- Intense vaginal itching
- Thick, white, curd-like vaginal discharge (cottage cheese-like)
- Redness and swelling of the vulva
- Burning sensation during urination
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- No foul smell (important distinguishing feature)
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is usually based on:
- Clinical symptoms
- Vaginal examination
- Vaginal swab or microscopy (KOH test)
- pH test (usually normal in yeast infection)
Treatment
Medical Treatment
- Antifungal vaginal creams or pessaries (Clotrimazole, Miconazole)
- Oral antifungal tablets (Fluconazole)
- Duration: 1–7 days depending on severity
Home Remedies
- Keep the genital area dry
- Wear loose cotton underwear
- Avoid scented soaps and vaginal douching
- Maintain good blood sugar control in diabetics
Complications
- Recurrent yeast infections (≥4 episodes/year)
- Severe vulvovaginal inflammation
- Increased discomfort during pregnancy if untreated
Prevention
- Avoid unnecessary antibiotics
- Maintain good genital hygiene
- Control diabetes
- Avoid tight clothing
- Use probiotics if prone to recurrent infections
When to See a Doctor
- First-time infection
- Symptoms not improving with treatment
- Recurrent infections
- During pregnancy
- If discharge has a foul smell or blood
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. Is vaginal yeast infection a sexually transmitted disease?
No. It is not classified as an STD, but it can sometimes be triggered by sexual activity.
Q2. Can yeast infection occur during pregnancy?
Yes. Hormonal changes during pregnancy increase the risk. Treatment should be taken only under medical supervision.
Q3. Does a yeast infection cause bad odor?
Usually no. Foul smell suggests another infection like bacterial vaginosis.
Q4. Can men get yeast infection from their partner?
Yes, men can develop balanitis (itching, redness of penis), though it is uncommon.
Q5. Can yeast infection go away on its own?
Mild cases may improve, but treatment is recommended to prevent worsening.
Q6. How long does treatment take?
Symptoms usually improve within 2–3 days, with complete cure in 7 days.
Q7. Can I use home remedies?
Home remedies may relieve symptoms but medical antifungal treatment is the most effective.
Q8. Why do yeast infections keep coming back?
Common reasons include diabetes, improper treatment, frequent antibiotics, or immune issues.
Conclusion
Vaginal yeast infection is common, treatable, and preventable. Early diagnosis and proper antifungal therapy ensure quick relief and prevent recurrence. If infections are frequent or severe, medical evaluation is essential.




